Table of Contents
Why are the Characteristics of Living Organisms Important?
All living organisms share 8 fundamental characteristics that allow them to survive, adapt, and interact with their environment. Understanding them helps us identify what makes something truly alive.
Biology is the study of living organisms, so to classify any organism as LIVING, they MUST perform these 8 processes.
We use the acronym MRS H GREN to represent these processes:
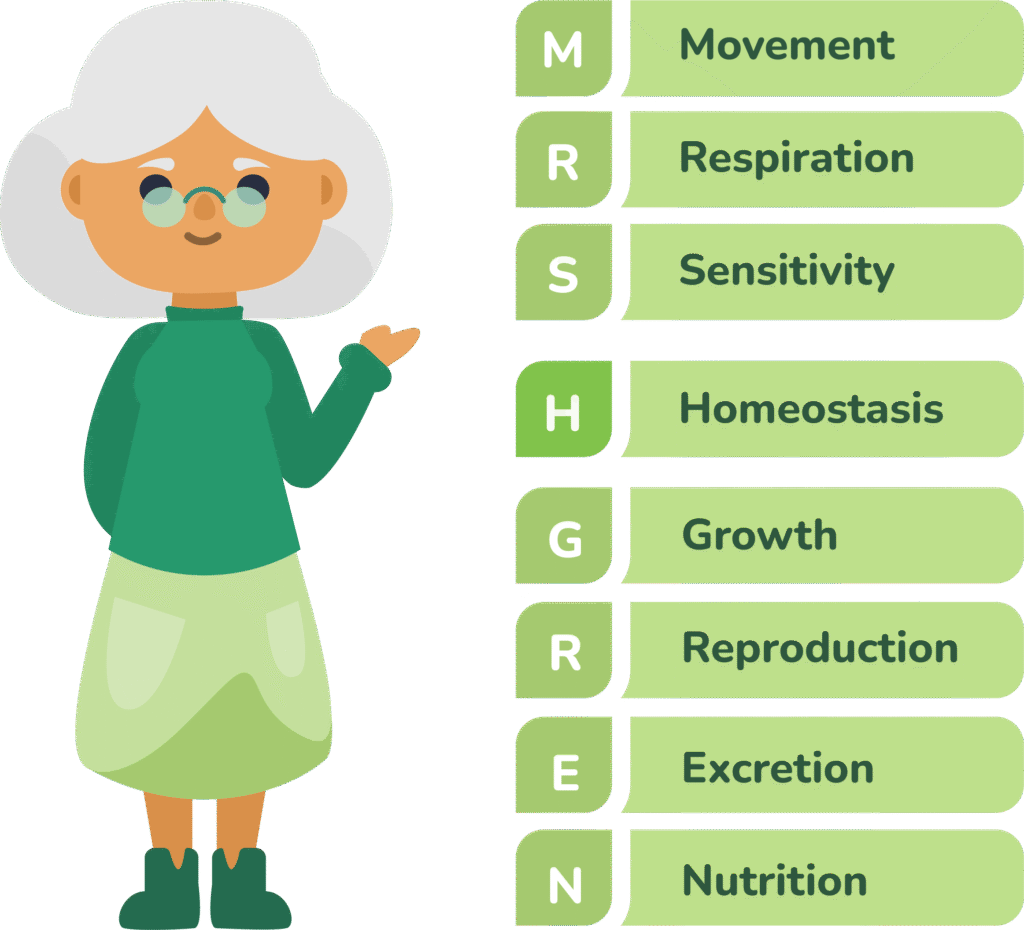
Movement
What is Movement?
Movement is the ability of living organism to change position.
Why Move?
Moving helps organisms find food, run from danger, and search for mates.

How Do Organisms Move?
Movement can take different forms across organisms. In animals, movement often involves muscle contractions, whilst plants change their orientation and grow towards sunlight (tropism) as a form of movement.
EXTRA: When organisms to move from one place to another this is called locomotion (eg. walking to to the kitchen)
Respiration
What is Respiration?
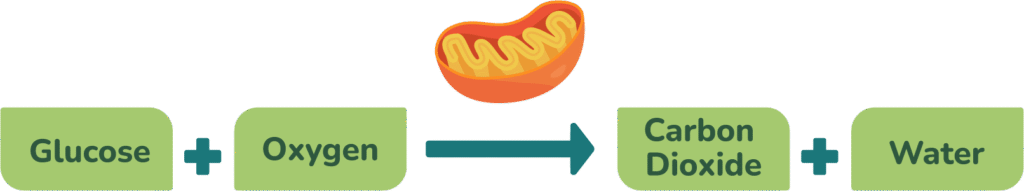
Respiration is a chemical reaction where glucose is broken down to release energy. This reaction mostly takes place in the mitochondria of cells.
Why Respire?
Respiration gives organisms the energy to live, grow, and move.
How Do Organisms Respire?
We can breakdown glucose to release energy either with oxygen (aerobic respiration) or without oxygen (anaerobic respiration).
“We release energy” means we produce a little molecule called ATP (adenosine triphosphate) which is the currency for energy (just like you pay your food with money, when we spend energy, we use ATP molecules).
Classification
Let’s try to picture every single organism that ever existed. They’re all so different, right? So, for us to study each one properly we have to group them by their similarities. But we’re not going to group all red or all yellow animals together, rather group organisms with similar morphology and genetics.
The first broad groups in biology are the five kingdoms: animals, plants, fungi, protoctists, and bacteria.
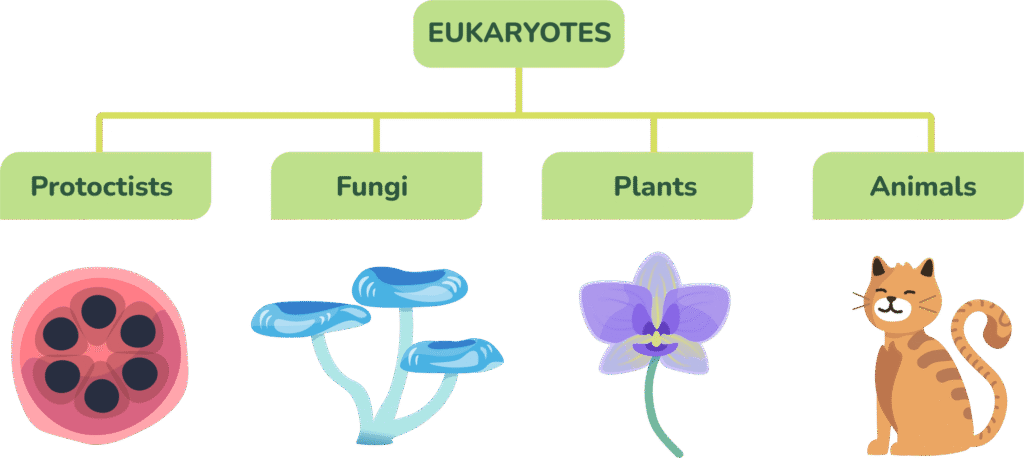
What Are Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes?
Eukaryote comes from Greek, meaning “true nucleus” and Prokaryote “before nucleus”.
So, we call organisms that have a nucleus (animals, plants, etc.) “Eukaryotes” and ones that don’t (bacteria) “Prokaryotes”.